Building 1, Block 4, Wufeng Industrial Park, Daxi Town, Taizhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
In the world of industrial automation and machinery, the three-phase asynchronous motor has emerged as a cornerstone technology, powering a vast array of equipment across multiple sectors. This motor type, also known as an induction motor, is favored for its simplicity, durability, and exceptional efficiency. With growing demands for energy-efficient and reliable equipment, the three-phase asynchronous motor is continuing to gain importance in modern industries. In this article, we will explore the key features, advantages, applications, and emerging trends surrounding three-phase asynchronous motors and how they are shaping the future of manufacturing and industrial power.
What is a Three-Phase Asynchronous Motor?
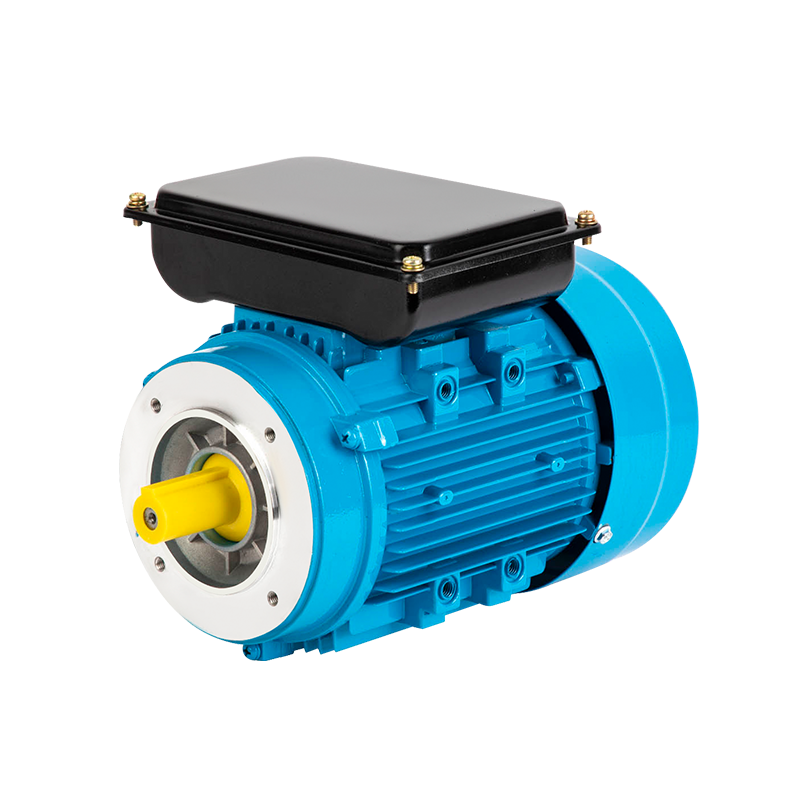
A three-phase asynchronous motor is a type of induction motor that operates using a three-phase electrical power supply. Unlike single-phase motors, which use a single alternating current (AC) supply, three-phase motors use three separate AC currents that are offset by 120 degrees from each other. This configuration creates a continuous and balanced rotating magnetic field that induces motion in the motor's rotor.
The term "asynchronous" refers to the fact that the motor’s rotor does not always rotate at the exact same speed as the magnetic field produced by the stator. The difference in speed between the rotor and the magnetic field, known as "slip," is crucial for the motor's operation and allows it to function effectively under varying load conditions.
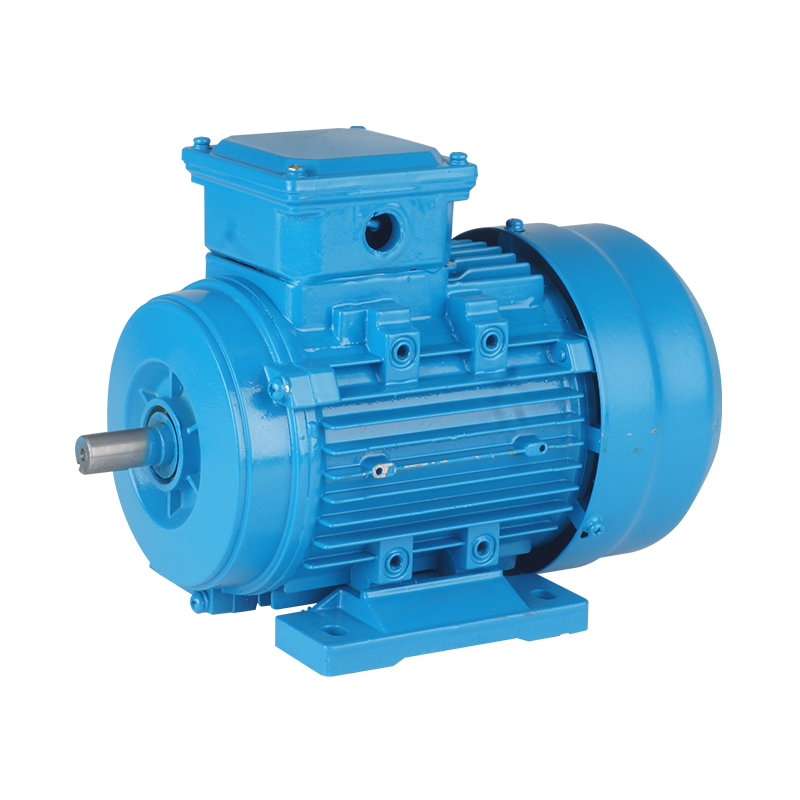

Three-phase asynchronous motors are renowned for their ability to handle high-power demands, making them an ideal choice for industries that require reliable, high-performance machinery. These motors are available in a wide range of power ratings, from small machines used in household appliances to massive industrial machines that power heavy equipment in factories and power plants.
Advantages of Three-Phase Asynchronous Motors
The three-phase asynchronous motor offers a variety of benefits that make it the preferred choice for numerous industrial applications:
High Efficiency: One of the primary advantages of the three-phase asynchronous motor is its exceptional efficiency. Because it operates on three-phase power, the motor delivers a more stable and continuous flow of energy, reducing energy losses compared to single-phase motors. This results in lower operational costs and reduced energy consumption, making it an attractive option for energy-conscious industries.
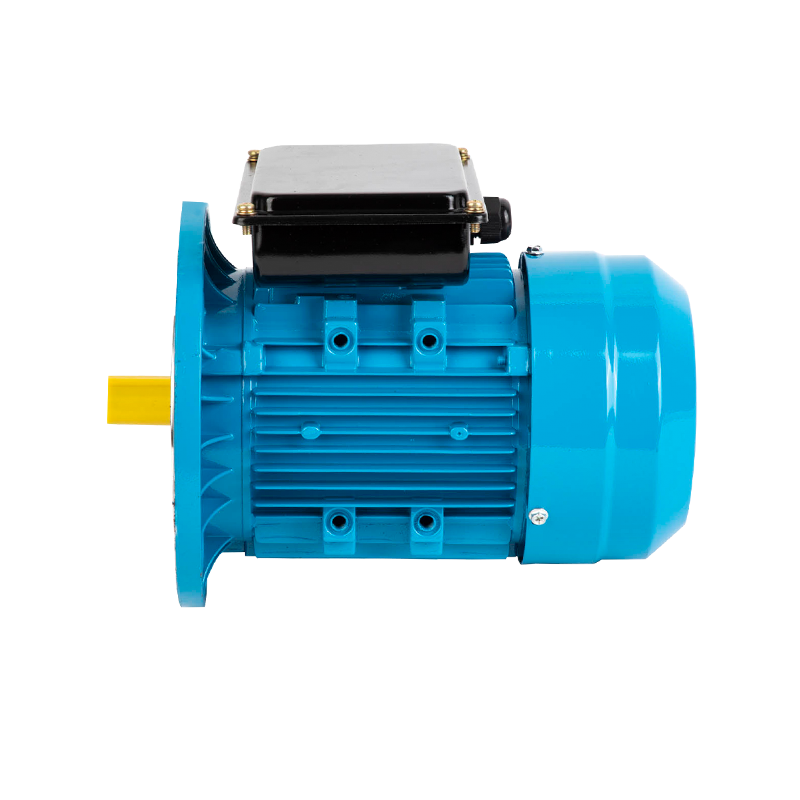
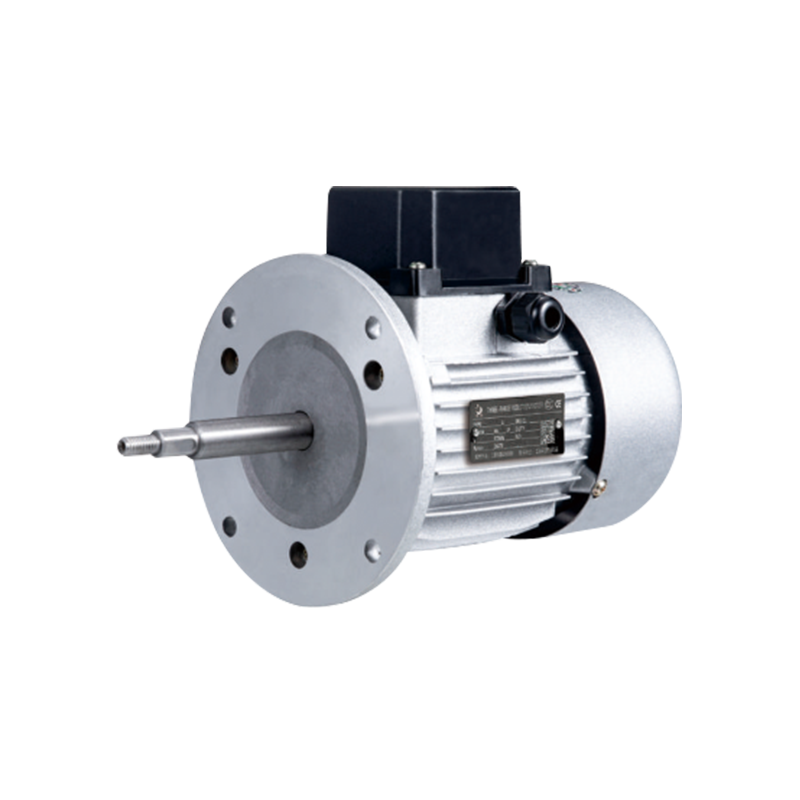
Simplicity and Durability: The construction of a three-phase asynchronous motor is relatively simple, consisting of a rotor, stator, and bearings. This simplicity translates into fewer components, making the motor easy to maintain and repair. As a result, these motors are highly durable and can withstand harsh working conditions, to long operational lifespans and minimal downtime.
High Starting Torque: Three-phase motors are known for their high starting torque, which allows them to power large loads from a standstill position. This feature is particularly important for industrial applications that require heavy machinery to be powered up and running quickly without stalling.
Smooth Operation: The three-phase power supply ensures that the motor runs smoothly and with minimal vibrations. This smooth operation translates into reduced wear and tear on both the motor and the equipment it powers, to longer service life and reduced maintenance costs.
Versatility: Three-phase asynchronous motors are highly versatile and can be used across a wide range of applications. They are suitable for both high and low-power requirements, from small-scale applications like fans and pumps to large industrial machines in manufacturing plants.
Key Applications of Three-Phase Asynchronous Motors
The versatility and efficiency of three-phase asynchronous motors make them suitable for a broad range of applications across multiple industries. Some of the common uses include:
Industrial Manufacturing: Three-phase motors are the go-to choice for driving machinery in factories, including conveyors, mixers, compressors, and crushers. Their ability to handle heavy loads and operate continuously makes them ideal for the demanding environments of industrial production lines.
HVAC Systems: In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, three-phase motors are used to power large fans, pumps, and compressors. The ability to run efficiently under varying loads ensures that HVAC systems can maintain performance, regardless of environmental conditions.