Building 1, Block 4, Wufeng Industrial Park, Daxi Town, Taizhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
Fans are widely used in homes, offices, factories, and vehicles, and at the core of every fan is the fan motor. Understanding what a fan motor is, how it works, and the types available can help users choose the right option for their applications.
What Is a Fan Motor?
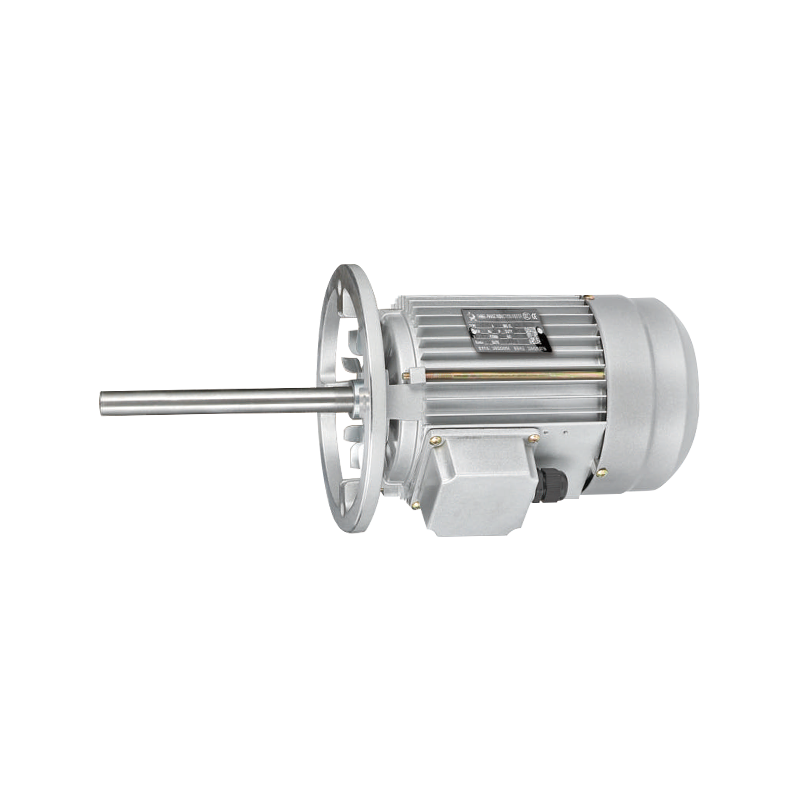
A fan motor is the component that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to rotate the blades of a fan. Driving the fan blades enables the movement of air, which can be used for cooling, ventilation, or circulation. Fan motors are used in many different products, from household ceiling fans and exhaust systems to industrial cooling equipment and automotive ventilation units.

The design of a fan motor depends on its intended use. For example, motors in small household fans are compact and optimized for quiet operation, while motors in industrial fans are built for higher torque and durability. Regardless of size or setting, the role of a fan motor remains the same: to provide the mechanical force necessary for air movement.
How Does a Fan Motor Work?
The operation of a fan motor is based on the principles of electromagnetism. When electrical current flows through the motor windings, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the rotor, causing it to turn. As the rotor spins, it rotates the fan blades attached to it, generating airflow.
In alternating current (AC) fan motors, the direction of current changes periodically, creating a rotating magnetic field that drives the rotor. In direct current (DC) fan motors, electronic circuits control the current to achieve rotation. Both AC and DC fan motors serve the same purpose but differ in efficiency, speed control, and noise characteristics.
Some fan motors include additional components such as capacitors, which help improve starting torque and efficiency. In modern designs, variable speed controls or electronic drivers are often integrated, allowing users to adjust airflow as needed.
What Are the Main Types of Fan Motors?
There are several types of fan motors, each designed for different requirements:
AC Fan Motors—Common in ceiling fans, exhaust fans, and industrial ventilation. They are reliable, widely available, and cost-effective.
DC Fan Motors—Often used in electronics cooling, automotive fans, and energy-efficient systems. They allow precise speed control, consume less power, and are generally quieter than AC motors.
Shaded Pole Motors—A simple type of AC motor often found in small appliances like table fans. They are inexpensive but less efficient compared to other motor types.
Brushless DC Motors (BLDC)—Increasingly popular in modern applications due to their long lifespan, efficiency, and low noise. These motors use electronic controllers instead of mechanical brushes.
Capacitor-Run Motors—Commonly used in ceiling fans, they provide smoother operation and improved efficiency compared to simple shaded pole motors.
The selection of a fan motor depends on the application’s needs, such as airflow volume, energy efficiency, noise level, and cost considerations.
A fan motor is an essential part of any fan system, providing the mechanical energy required to move air. It operates through electromagnetic principles, converting electrical energy into rotational motion that drives the blades. Different types of fan motors, including AC, DC, shaded pole, and brushless designs, are available to suit various applications.
By understanding what a fan motor is, how it works, and the main types available, users can make informed choices when selecting fans for residential, commercial, or industrial use. This knowledge also helps in maintenance, troubleshooting, and upgrading to more efficient technologies when necessary.